Knowing the Difference Between Sunspots & Pigmentation?
While there are many words that can be used to describe pigmentation (hyperpigmentation, age spots, liver spots, and even sunspots) there is actually a big difference between a sunspot (also known as solar keratosis) and pigmentation.
A sunspot is a rough, scaly, raised patch of skin usually less than 2.5cm in diameter. A sunspot develops from years of exposure to the sun and is most commonly found on areas exposed to the sun such as your face, lips, ears, back of your hands, forearms, scalp, or neck.
A sunspot enlarges slowly and usually causes no other signs or symptoms other than the raised scaly patch of skin. As they take so long to develop, they usually appear on people over 40 years of age.
The colour underneath the scaly skin can appear as pink, red, or brown, and in some cases, it can feel like it has a hard, wart-like surface.
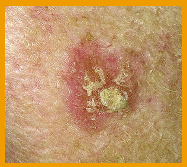
Sunspot risk factors
Anyone can develop a sunspot, but you may be more likely to develop the condition if you:
Are older than 40
Live in a sunny place
Have a history of frequent or intense sun exposure or sunburn
Have red or blond hair, and blue or light-colored eyes
Tend to freckle or burn when exposed to sunlight
Have a personal history of a solar keratosis or skin cancer
Have a weak immune system as a result of chemotherapy, leukemia, AIDS or organ transplant medications
You can treat sunspots with John Plunkett’s Sunspot Cream with Salicylic Acid which works to gradually soften and remove the unwanted skin tissue.
Pigmentation, on the other hand, is defined as a flat darkened area on the skin, there is no change to the texture, it is just a change in colour. This can show as either a mild darkening on a patch of skin (mild pigmentation) or as a very dark patch of skin (hyperpigmentation). These patches can vary in size and develop anywhere on the body; however, you usually find them on areas that are most exposed to the sun.
The main risk factors for developing pigmentation is exposure to the sun, inflammation, trauma to the skin (such as a burn, graze or acne), hormone changes (such as pregnancy or the oral contraceptive), drugs that make you more sensitive to sunlight and darker skin types which are more prone to pigmentation changes.
The pigmentation is caused by an excess production of melanin which is what makes it appear darker than the rest of the skin.
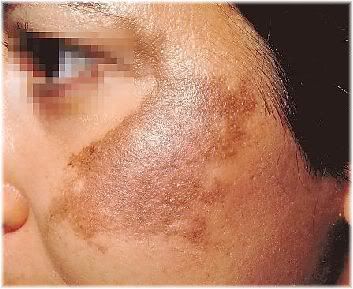
There are many ingredients which can assist with fading or removing excess melanin; however, it is best to use a product which will suit the kind of pigmentation you have. To find out more about pigmentation and the solutions available for the varied pigmentation levels, go to superfade.com.au/about-pigmentation/.
Now that you know the difference between a sunspot and pigmentation, you will be able to make the best decisions on treatment. Ask a doctor if you are concerned about a spot on your skin, a pigmented spot or mole that has recently become darker, changed colour, become enlarged, itchy or bleeds. If symptoms worsen or change unexpectedly, talk to your healthcare professional.


